How to have ‘the vape talk’ with your kids
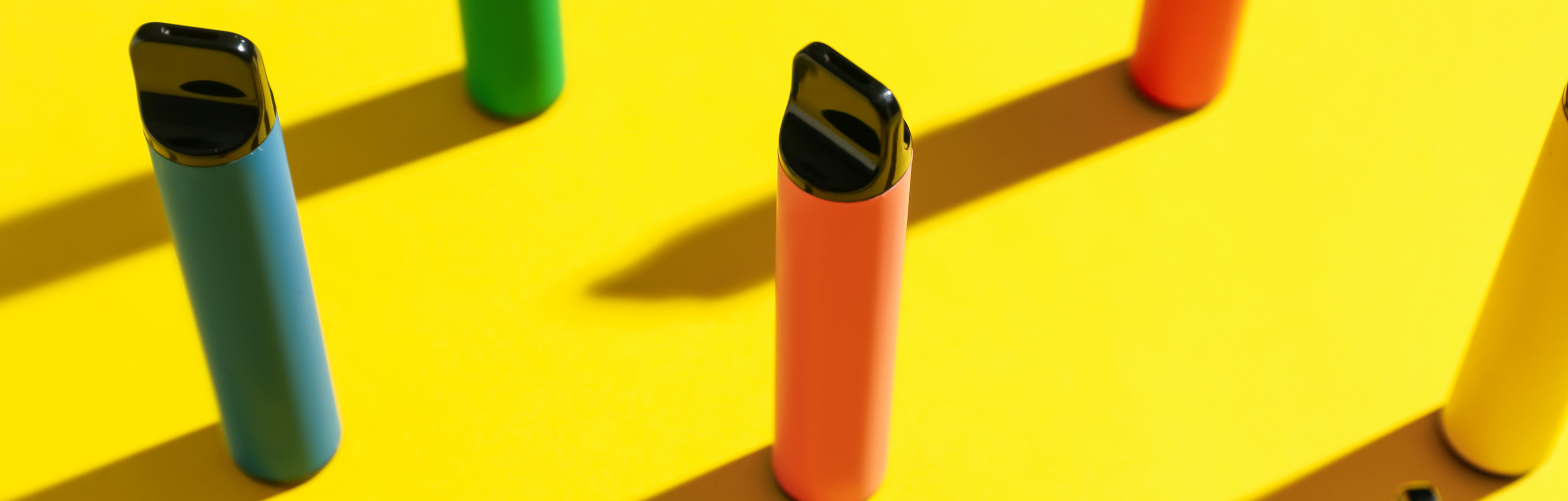

E-cigarettes, vapes, stigs, pods… they go by many names and they pose a health risk to our young people.
As parents and carers, it is important to talk about vaping with our children and teens. By being available to have these conversations with our kids, we build connections and trust, and empower them to make healthier and safer choices in the future.
What are e-cigarettes (vapes) and how are they used?
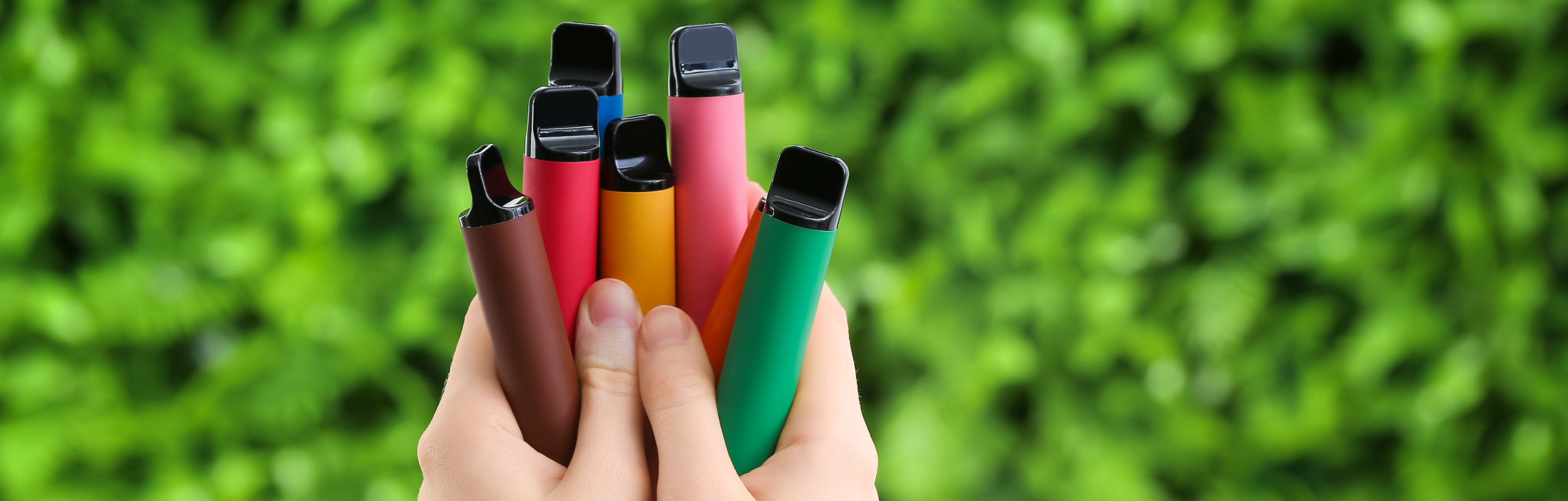
E-cigarettes are battery-powered devices that mimic the process of smoking by heating an e-liquid into a vapour. The vapours are inhaled and exhaled. This is known as ‘vaping’. The vapour can be odourless or scented with added flavourings and scents. E-cigarettes can look like traditional cigarettes, cigars or everyday items such as USBs or pens. In Australia, the most common e-cigarettes are small disposable plastic devices.
What is in e-cigarettes?
Most vaping products are produced in countries without regulations, so it’s difficult to know exactly what they contain. In fact, a study on more than 50 vape “juices” available in Australia found none of them had accurate ingredient lists. Research revealed vapes contain many toxic chemicals, including nicotine, formaldehyde, and propylene glycol.
Do e-cigarettes contain nicotine?
E-cigarette products bought in Australia are not legally allowed to contain nicotine but if purchased somewhere else (eg online or overseas) they may contain nicotine because labelling may not be regulated. Nicotine is a highly addictive chemical. The level of nicotine in vapes can be very high, and there is evidence that some people have experienced seizures after inhaling highly concentrated levels of nicotine.
What are the health risks?
Vaping is not a safe activity and is potentially dangerous. Our lungs are designed to breathe air, not the nicotine, artificial flavourings, and chemicals commonly found in e-cigarettes.
Vaping has been linked with symptoms including persistent coughing, airway irritation, heart palpitations, chest pain, nausea, vomiting, burns, and seizures. People who have used vapes also report that it impacts their health, fitness and lung capacity.
How many young people are using e-cigarettes?
Recent Government figures show rising rates of vaping among under 25s. Eleven per cent of people aged 16 to 24 reported being a current user of e-cigarettes, or “vapes”, more than double the number in 2020.
Young people tend to see vaping as a “normalised” behaviour and incorrectly believe that most secondary school students are vaping. It can be useful to highlight that the majority of their peers are not vaping regulalry.
Can e-cigarettes lead to tobacco smoking?
E-cigarettes may normalise the act of smoking and attract young people. E-cigarette use familiarises users to traditional smoking behaviours such as inhalation, exhalation, and even holding a cigarette. This means that even if young people use e-cigarettes without the nicotine, the smoking-related behaviours they pick up make it more likely they will transition to cigarette smoking.